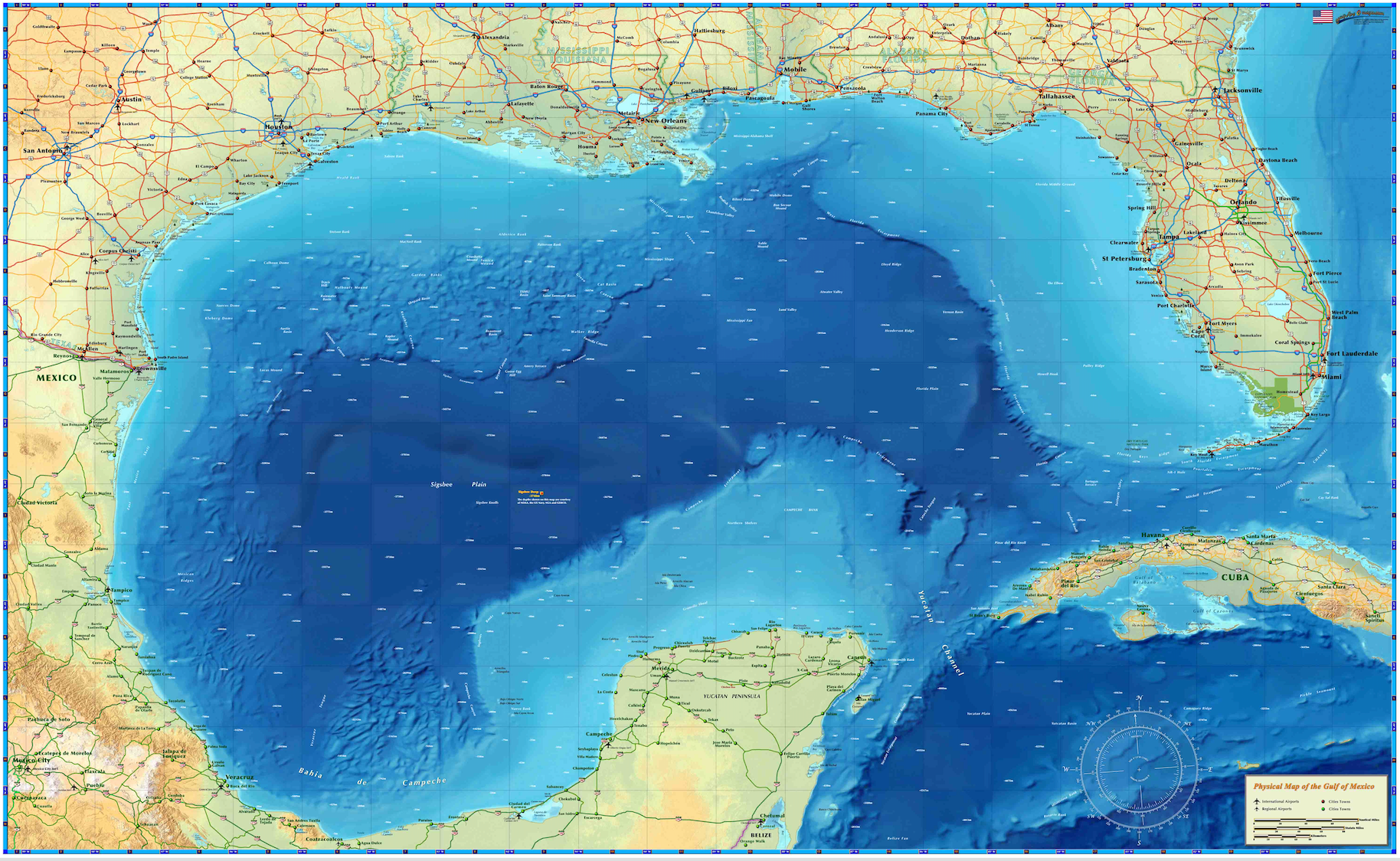
The Gulf of Mexico is one of the most significant and diverse marine environments in the world. Spanning over 600,000 square miles, it serves as a vital resource for millions of people and countless species of marine life. From its rich biodiversity to its role in global trade, the Gulf of Mexico remains an essential component of our planet's natural and economic systems.
As a cradle of life, the Gulf supports a wide range of ecosystems, including mangroves, coral reefs, and wetlands. These habitats not only sustain marine biodiversity but also provide essential services such as water filtration, coastal protection, and carbon sequestration. Understanding the Gulf’s ecological significance is crucial for preserving its health and ensuring its sustainability for future generations.
Beyond its ecological importance, the Gulf of Mexico plays a pivotal role in the economies of the United States, Mexico, and Cuba. Its vast oil reserves, fisheries, and shipping routes contribute significantly to regional and global commerce. However, the Gulf faces challenges such as pollution, climate change, and overfishing, which threaten its delicate balance. This article delves into the multifaceted nature of the Gulf of Mexico, exploring its geography, ecology, economic contributions, and the challenges it faces.
Read also:Arlington The Vibrant City That Has Something For Everyone
Table of Contents
- Geography of the Gulf of Mexico
- Ecosystems and Biodiversity
- Economic Contributions of the Gulf
- Climate Change and Its Impact
- Pollution Challenges in the Gulf
- Conservation Efforts
- Oil Industry in the Gulf
- Fishing and Aquaculture
- Tourism and Recreational Activities
- The Future of the Gulf of Mexico
Geography of the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico is a semi-enclosed sea bordered by the United States, Mexico, and Cuba. It stretches across approximately 615,000 square miles, making it one of the largest water bodies in the Western Hemisphere. The Gulf is defined by its unique geography, with the Mississippi River Delta serving as a central feature that influences its sedimentation and water flow patterns.
Coastal Features
One of the most prominent features of the Gulf is its extensive coastline, which includes marshes, barrier islands, and beaches. These coastal areas provide critical habitats for numerous species and act as natural barriers against storms and hurricanes. The Gulf’s coastline is particularly vulnerable to erosion and rising sea levels, posing significant challenges for coastal communities.
Depth and Currents
The Gulf of Mexico varies significantly in depth, with the deepest point reaching about 14,383 feet. Its currents, such as the Loop Current, play a crucial role in regulating water temperatures and facilitating the movement of marine life. These currents also influence weather patterns, contributing to the formation of hurricanes that frequently impact the region.
Ecosystems and Biodiversity
The Gulf of Mexico hosts an incredible array of ecosystems, each contributing to its rich biodiversity. From vibrant coral reefs to expansive seagrass beds, these habitats support a wide variety of marine species, including fish, turtles, dolphins, and sharks.
Coral Reefs
Coral reefs in the Gulf of Mexico are vital for maintaining marine biodiversity. They provide shelter and breeding grounds for numerous species and serve as natural breakwaters that protect coastlines from erosion. However, coral reefs face threats from pollution, climate change, and ocean acidification, which have led to widespread degradation.
Seagrass Beds
Seagrass beds are another critical component of the Gulf’s ecosystems. These underwater meadows support a diverse array of marine life and help improve water quality by filtering pollutants. Seagrass beds also act as nurseries for many commercially important fish species, underscoring their economic significance.
Read also:Eric Stonestreet A Comprehensive Look At The Talented Actors Life And Career
Economic Contributions of the Gulf
The Gulf of Mexico is a powerhouse of economic activity, supporting industries such as oil and gas, fishing, and tourism. Its strategic location and abundant natural resources make it a vital component of the global economy.
Oil and Gas Industry
The Gulf of Mexico is home to some of the largest oil reserves in the world, with offshore drilling contributing significantly to the energy sector. The region produces approximately 17% of the United States’ total crude oil output, making it a crucial player in meeting domestic energy demands.
Fishing and Seafood
Commercial fishing in the Gulf of Mexico supports thousands of jobs and generates billions of dollars annually. The region is renowned for its shrimp, oysters, and blue crabs, which are staples in the global seafood market. However, overfishing and habitat destruction pose significant threats to the sustainability of these fisheries.
Climate Change and Its Impact
Climate change poses a growing threat to the Gulf of Mexico, affecting its ecosystems, economies, and communities. Rising sea levels, increasing water temperatures, and more frequent extreme weather events are altering the Gulf’s natural dynamics and challenging its resilience.
Sea Level Rise
As global temperatures rise, sea levels in the Gulf of Mexico are expected to increase, leading to the inundation of low-lying coastal areas. This phenomenon threatens coastal habitats and infrastructure, necessitating adaptive measures to mitigate its impacts.
Extreme Weather Events
Hurricanes and tropical storms in the Gulf of Mexico have become more intense and frequent due to climate change. These events cause significant damage to coastal communities and disrupt economic activities, highlighting the need for improved disaster preparedness and response strategies.
Pollution Challenges in the Gulf
Pollution remains a persistent issue in the Gulf of Mexico, with agricultural runoff, industrial discharge, and oil spills contributing to its degradation. These pollutants harm marine life, degrade habitats, and compromise water quality, affecting both human health and the environment.
Agricultural Runoff
Agricultural runoff from the Mississippi River Basin introduces excessive nutrients into the Gulf, leading to the formation of harmful algal blooms and dead zones. These dead zones, areas with low oxygen levels, can devastate marine ecosystems and impact fisheries.
Oil Spills
Oil spills, such as the Deepwater Horizon disaster in 2010, have had catastrophic effects on the Gulf’s environment and economy. The spill caused widespread damage to marine habitats and disrupted local industries, emphasizing the need for stricter safety regulations and more effective cleanup technologies.
Conservation Efforts
Efforts to conserve the Gulf of Mexico focus on protecting its ecosystems, reducing pollution, and promoting sustainable practices. Governments, organizations, and communities are working together to address the challenges facing the Gulf and ensure its long-term health.
Protected Areas
Establishing marine protected areas is a key strategy in conserving the Gulf’s biodiversity. These areas limit human activities such as fishing and oil drilling, allowing ecosystems to recover and thrive. Protected areas also serve as valuable research sites for scientists studying marine life.
Sustainable Practices
Promoting sustainable fishing, reducing plastic waste, and improving wastewater management are essential steps in protecting the Gulf of Mexico. By adopting eco-friendly practices, individuals and industries can help preserve the Gulf’s natural beauty and resources for future generations.
Oil Industry in the Gulf
The oil industry in the Gulf of Mexico is a double-edged sword, providing economic benefits while posing environmental risks. Advances in technology and stricter regulations aim to balance the need for energy with the imperative to protect the Gulf’s fragile ecosystems.
Offshore Drilling
Offshore drilling in the Gulf has revolutionized the energy sector, providing a reliable source of oil and gas. However, the environmental risks associated with drilling, such as oil spills and habitat disruption, require careful management and monitoring to minimize their impact.
Renewable Energy
As the world transitions to cleaner energy sources, the Gulf of Mexico is increasingly being explored for its potential in renewable energy, particularly wind and solar power. These alternatives offer a promising pathway to reducing the Gulf’s reliance on fossil fuels while supporting economic growth.
Fishing and Aquaculture
Fishing and aquaculture in the Gulf of Mexico are vital for food security and economic development. However, sustainable practices are necessary to ensure the long-term viability of these industries and the health of the Gulf’s ecosystems.
Sustainable Fishing Practices
Implementing sustainable fishing practices, such as catch limits and seasonal closures, helps maintain fish populations and protect marine habitats. By adhering to these practices, fishermen can contribute to the conservation of the Gulf’s resources while ensuring their livelihoods.
Aquaculture Development
Aquaculture, or fish farming, is gaining prominence in the Gulf as a means of meeting growing seafood demand while reducing pressure on wild fish stocks. Advances in aquaculture technology and management are making it a more environmentally friendly and economically viable option.
Tourism and Recreational Activities
The Gulf of Mexico attracts millions of tourists each year, drawn by its stunning beaches, vibrant culture, and recreational opportunities. Tourism contributes significantly to the region’s economy, supporting jobs and businesses in coastal communities.
Beach and Coastal Tourism
Beaches along the Gulf Coast are among the most popular tourist destinations in the world. Activities such as swimming, sunbathing, and water sports draw visitors from all over, boosting local economies and promoting cultural exchange.
Ecotourism
Ecotourism in the Gulf of Mexico offers visitors the chance to explore its unique ecosystems while supporting conservation efforts. Activities such as birdwatching, snorkeling, and nature tours provide an educational and immersive experience that fosters appreciation for the Gulf’s natural wonders.
The Future of the Gulf of Mexico
The future of the Gulf of Mexico depends on the collective actions of governments, organizations, and individuals to address the challenges it faces. By prioritizing conservation, sustainability, and innovation, we can ensure the Gulf remains a thriving and vibrant region for generations to come.
Technological Advancements
Advances in technology offer promising solutions to many of the Gulf’s challenges, from improving oil spill cleanup methods to enhancing renewable energy production. Investing in research and development can drive innovation and create new opportunities for economic growth and environmental protection.
Community Engagement
Engaging local communities in conservation efforts is crucial for the success of any initiative aimed at protecting the Gulf of Mexico. By empowering individuals to take action and fostering a sense of stewardship, we can build a collective commitment to preserving the Gulf’s natural and cultural heritage.
Conclusion
The Gulf of Mexico is a remarkable natural wonder that plays a vital role in shaping ecosystems, economies, and cultures across the region. Its rich biodiversity, abundant resources, and strategic importance make it an invaluable asset for millions of people. However, the Gulf faces significant challenges that require urgent attention and action.
By addressing issues such as climate change, pollution, and overfishing, we can ensure the Gulf remains a thriving and sustainable environment. It is our responsibility to protect this invaluable resource and promote practices that benefit both people and the planet.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences regarding the Gulf of Mexico in the comments below. Your feedback and insights can help us better understand the issues facing this vital region and inspire others to take action. Together, we can make a difference in preserving the Gulf’s natural beauty and ecological significance for future generations.